Defining Roles, Responsibilities and Skills in Project Staffing Plan
 The purpose of a project staffing plan is to make certain that the project is provided with sufficient human resources that possess the talents, knowledge and experience required for successful work completion. Roles, responsibilities and skills are the key elements that compose the plan and thereby should be considered with great care. The following article provides common definitions of project role, responsibility and skill and briefly describes how to plan project staffing needs by considering these definitions.
The purpose of a project staffing plan is to make certain that the project is provided with sufficient human resources that possess the talents, knowledge and experience required for successful work completion. Roles, responsibilities and skills are the key elements that compose the plan and thereby should be considered with great care. The following article provides common definitions of project role, responsibility and skill and briefly describes how to plan project staffing needs by considering these definitions.
Defining Project Roles
A project role defines an expected behavior associated with a particular job or status of an individual or group participating in a given project.
Using role-based models in project staffing and management is a flexible way to associate participants with particular task assignments and responsibilities, so that each individual/group will be expected to act within the scope and content of the assigned role. This approach enables clarity, speed and predictability in collaborative interactions between staff members throughout the course of work. Sample roles are Sponsor, Project Manager, Customer, Team Leader, Team Member, Steering Committee, Vendor, Facilitator.
Temporary and Permanent Roles
By definition, a job description is similar to a project role. Just like a team member can be assigned to one or more jobs at the same time, this person can carry out several roles, which can be temporary (coming up under certain circumstances) and permanent (lasting throughout the entire project lifecycle). For example, one individual can perform the role of team leader from the very beginning till the project’s end and also be expected to carry out some temporary roles in parallel (e.g. subject matter expert and business analyst) during the planning stage. When this stage is over, the employee will relinquish the temporary roles and focus on the core team leadership duties.
It should be noted that sometimes temporary roles are not included in project staffing plan (as they’re described in supporting documentation instead), while only key and permanent roles are listed there. This matter depends on the specificity and staffing requirements defined by the business organization that runs and manages the project.
Defining Staff Responsibilities
Responsibilities determine a suite of duties or obligations an individual needs to perform to satisfactorily complete an assigned job or task, while acting within the scope and content of the related role.
When a team member gets appointed to a role on the project, he or she is given a certain responsibility and also authorized to take action or make decisions that are not denied by the assigned role. Basically, project staff responsibilities specify respective roles and authorities.
Responsibilities vary from project to project. Meanwhile, there are several common groups of responsibilities that are common to most projects and that represent the steps and stages of the project management process, as follows:
- Conceptualizing: the basic duties and assignments for creating, justifying and approving project concept, defining the scope of work (incl. the baseline constraints of time, budget, quality), and initiating the work.
- Planning: a series of roles and associated responsibilities intended for developing effective plans (incl. staffing plan template) and determining the best possible course of action for the project.
- Implementing: the duties for implementing the general project plan and doing all tasks and activities relating to the execution process.
- Controlling: a range of responsibilities targeted to progress oversight, team coordination, goal tracking, status reporting, deliverables quality assurance, change control, and the like.
- Terminating: closing out each incomplete activity and related artifacts when the project objectives are completed and the deliverables are handed over to the customer.
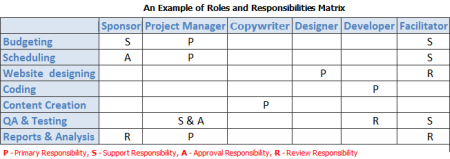
RRM – Roles and Responsibilities Matrix
After all roles and related duties are identified and defined, it is a best practice to combine this information into a single document that can be shared among all personnel concerned. Particularly, a roles and responsibilities matrix (RRM) can be created to point out which activity categories the participants will be assigned to, how they can interact with each other within the scope of their roles and authorities, and what duties they’re expected to carry out throughout the project lifecycle. Note that RRM says nothing about exact employee assignments but only represents a legend of project staffing needs. A simple example of RRM designed in MS Excel is given below.
Evaluating Employee Skills
The skills of an employee represent the suite of abilities, capacities and talents possessed and applied by that individual to carry out assigned roles and responsibilities.
Evaluation of employee skills against certain requirements lets determine whether project staff members are able to perform their roles and duties effectively and efficiently. Skills evaluation is a critical component of the staffing plan process because it enables to consider knowledge/skill factors in selecting right personnel with sufficient competence required for success achievement.
Factor Analysis to Address Project Staffing Needs
The way to evaluate employee skills and select people who have right knowledge and talents for a project is through conducting a factor analysis. According to such an analysis, for each candidate to a project role a compliance profile needs to be created in which the candidate’s skills and knowledge are ranked against a group of requirements (or factors) that best represent the staffing needs. Then, using the ranks in the candidate’s profile the evaluator can build a spider chart that visualizes the skills level against the baseline factor grade. After all candidates are evaluated, the evaluator needs to compare their spider charts and select those individuals that have demonstrated grades closest to the baseline.
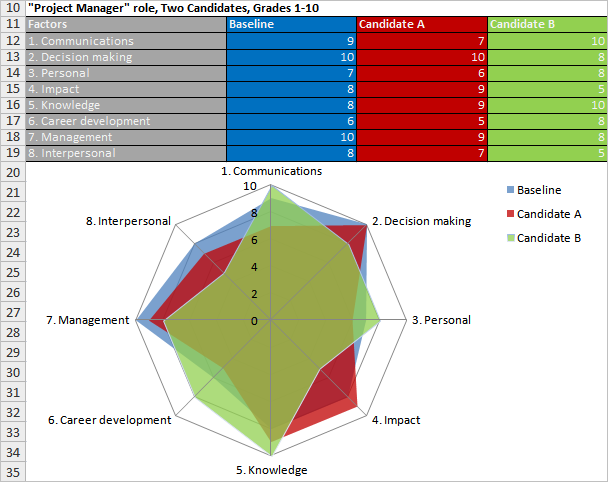
Note that because each particular project is unique and built around specific staffing plan requirements, this project will represent a specific baseline factor level which differs from other projects. The baseline factor level should be defined and described by experts at the beginning of the skills evaluation process.