Do you have a project that’s taking forever to complete? Are you wondering why nothing seems to be happening and when your project will wrap up? Then you’ve asked yourself, what is a project schedule and why work scheduling is important in the world of project management.
In this guide, we’ll delve into what a project schedule is and how project scheduling can help your team get through the obstacles that come with any long-term work. We’ll also provide step-by-step instructions on how to create a detailed schedule for your own project.
Learn about everything from developing the work breakdown structure (WBS) to project timeline and critical paths. We guarantee that by following the guidelines in this article you’ll be able to effectively schedule your next major undertaking.
What is a Project Schedule?
While you may have heard that “a schedule is just a plan”, sometimes just having a plan isn’t enough to get something done. A plan is not always specific enough to elaborate in detail what needs to be completed on time.
That’s where project scheduling comes in.
In project management, scheduling means a process of planning project activities. It is an integral part of the project management process, and a critical tool that helps you schedule your entire project from start to finish.
Schedules are created by breaking up all major segments of projects into shorter, more manageable steps or pieces called activities.
According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), the leading professional organization that determines industry best practices in project and program management, a project schedule defines “a time-ordered list of activities that describes the work to be executed by the project team to achieve specific goals and create specific deliverables.”
This definition is about as straightforward as it comes. It instructs you exactly what a project schedule is—a time-ordered list of everything you need to do—as well as how it can help you meet your goals.
Examples of project schedule definitions in different project methodologies:
1) In agile development environments (Scrum, eXtreme Programming), a project schedule refers to a high-level representation of the product roadmap that incorporates the required features and specifications and prioritizes the deliverables communicated to the customer.
In its simplest form, an agile project schedule is what is known as a sprint plan. Based on agile planning principles, sprint plans are time-boxed and prioritize task lists based on their value to the overall project planning objectives. A sprint schedule may be used by agile teams at any point in development or delivery, but this document should be referenced when scheduling events in an agile environment within an organization.
2) In traditional waterfall models (PRINCE2, PMBOK), a project schedule defines a step by step plan of all activities (tasks) and milestones to outline how the overall project will be developed in the most effective way. Particularly, the PRINCE2 project schedule contains time estimates for each step, which can be discounted or overestimated to provide sufficient lead-time for all work.
3) In lean methodologies like the Deming Cycle and Six Sigma, project schedules define the list of tasks required for completing and delivering goods and services that meet customers’ needs at minimum cost with high quality at the shortest time through continuous improvement of processes.
Types of Project Schedule
There are five common types of project schedules in use, each with its own ideal scenario. The following list briefly describes each schedule type.
- Gantt charts. Gantt charts are a traditional project schedule that also incorporate bar chart elements, which can be useful for visualizing project timeframes. The Gantt chart is one of the most popular project scheduling software applications available today. They are typically used for projects with a longer timeframe or more complex timeline management system.
- Kanban boards. Kanban boards are a great project schedule tool for teams who prefer to schedule out their activities in a more agile way, without the use of time estimates. In this type of project schedule, all tasks are listed on a wall or bulletin board in the order that they need to be completed.
- Critical path charts. In project time management, critical path defines the longest path of all the activities scheduled. In case the project cannot be completed within time, this is where you will find out where exactly it might break down. Critical path charts (network diagrams) provide information about timing and effort required to complete the projects.
- Agile sprint schedules. In agile development, repeatable activities are grouped into sprints and then given a time estimate that is worked into the schedule. For example, in a project to build a mobile application, planning out all envisioned deliverables and how they will be achieved is an effective use of agile sprint schedules. This type of project schedule can be used at any point during the life cycle of your project if you are using agile methodologies.
- PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique). PERT is one of the most common techniques for planning, scheduling and tracking projects. For example, in construction project management, PERT schedules are very helpful in planning out the timing for tasks such as pouring concrete, laying asphalt and starting new construction on a project.
Gantt Charts in Project Scheduling
In project schedule management, Gantt charts are the most commonly used method of visualizing work progress, timelines, activities and dependencies.
A Gantt chart is a graphic representation of a project schedule (often referred to as a “project calendar”) organized in a bar chart or a table that visualizes different phases of the work taking place throughout each day/week/month. The Gantt chart reveals the start and finish dates of project activities, the total length of time for completing tasks, and dependencies among various tasks.
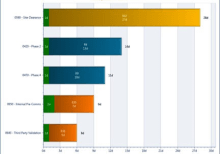
Below is an example of a project schedule Gantt chat:
Source: addonforge.com
Gantt chart is a traditional project scheduling tool. It helps project managers and stakeholders to visualize, analyze and track work progress. The primary reason for creating a project Gantt chart is to simplify the complexity of project management process by separating out tasks and assigning the start and finish dates to each one.
Below are several popular tools for creating Gantt chart schedules:
- Microsoft Project: For creating and editing Gantt charts (free and paid versions) and scheduling and tracking projects, including templates for particular industries such as manufacturing, construction, legal, more.
- Monday.com: A web-based scheduling tool for jobs and projects; both free and paid versions are available.
- TeamGantt: it is a team and task management software for businesses. It includes a Gantt Chart option that allows you to create charts with different custom views of your tasks.
- GanttPro: perhaps, one of the most affordable project scheduling software systems available for both individual and enterprise users. It is known to cost around $10 for a basic user account.
- SmartDraw: it is a professional alternative to Microsoft Project, which allows you to create more elaborate project schedules. SmartDraw is more flexible than MS Project and is able to handle and visualize tasks with multiple dependencies.
Work Breakdown Structure
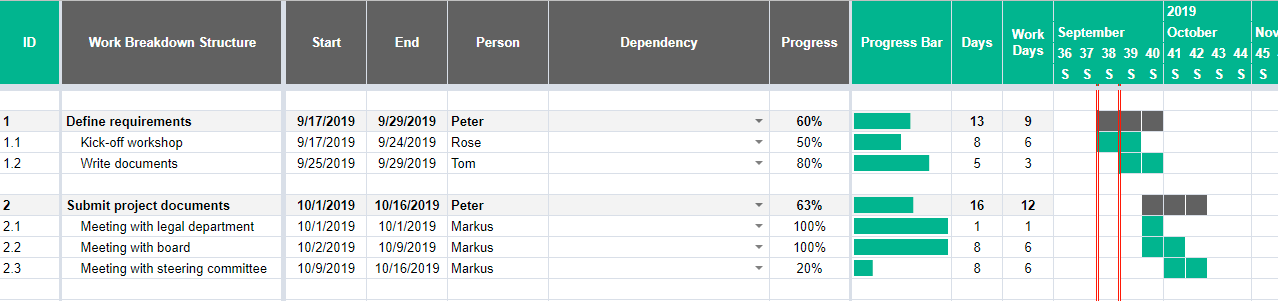
To create a Gantt schedule, you have to first come up with the work breakdown structure (WBS) for your project.
A WBS is a hierarchical structure of all tasks that need to be accomplished in order to complete a project. It breaks down major milestones of a project into more manageable portions – activities – and describes the relationships between the activities in detail. In other words, a WBS can be used to outline project deliverables as well as any steps that need to be taken in order to create those deliverables.
A WBS specifies the scope of a project including major components and their respective roles and tasks. It defines the deliverables that your project will create as well as the order in which those tasks are to be completed.
Here is a WBS example:
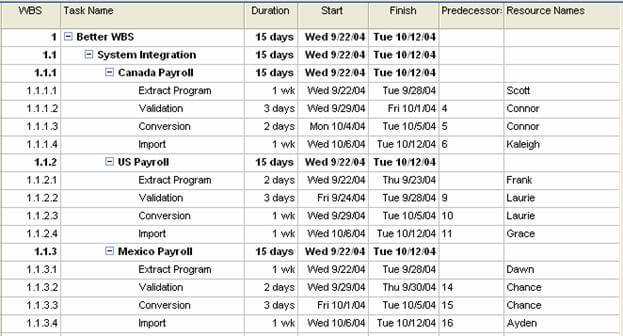
Source: tacticalprojectmanagement.com
One of the benefits of breaking down projects into smaller work pieces is to provide greater visibility into the responsibilities of each team member. While complicated projects or programs may have dozens or even hundreds of activities, a general rule for creating a work breakdown template is that all items must be organized into manageable pieces of work that can be completed in a reasonable time period, e.g. one week.
How to Create a WBS Spreadsheet in 3 Steps
There are several methods to creating WBS templates, but the most common is by using a spreadsheet. For example, use Google Spreadsheet or MS Excel.
The first step is to create a new spreadsheet, with one column for each major project activity or task.
The next step is to add sub-tasks and dependencies for each of the work packages beneath each main task, based on the breakdown template that is appropriate for your project. Generally, most activities will have three to eight levels of sub-tasks beneath them.
When creating sub-tasks, you want to ensure that they are not too broad or too narrow in description. For example, you would not want the task “Write a report” as a sub-task because it is too broad. But you also would not want to have “Write a report on marketing strategy for the year” as a sub-task because it is too narrow.
The last step is to assign a responsible party, i.e., a team member, to each of your tasks and sub-tasks. By doing this, you will create accountability within your project management schedule, which can help keep things running smoothly.
Now, your WBS spreadsheet is ready to go – all you have to do is insert this template into your project schedule Gantt chart.
Critical Path in Project Scheduling
To complete a project, you have to have a clear picture of how the tasks will get executed and by which team member. In order to plan effectively, you’ll need to know the critical path for each task.
The critical path is the sequence of activities necessary to deliver a product or service on time and according to specifications.
The critical path is used in project scheduling, i.e., knowing the time and resources needed to complete each task, since it helps you clearly understand what needs to be done in order for a project or program to be successfully completed.
For instance, if you have a series of ten tasks that each takes ten days to complete, then it’s very easy to understand that the entire project will take 100 days for completion. What makes this system different from others is that you can use it with any number of resources, not just time-based resource allocation, since it uses calendars of all types.
Critical Path Schedule
A critical path chart (CPC) is an extension of the Gantt chart, but it also includes the earliest start date (ESD) for each activity, as well as the latest start date (LSD), which is also referred to as the latest finish date (LFD).
The ESD represents how much time it will take to complete an activity once its predecessor or successor activities have started. Similarly, the LSD represents the amount of time before an activity should be started in order to finish on schedule. A project schedule that includes the ESD and LSD calculations for each activity is referred to as a critical path summary.
Critical path schedule / diagram is the definitive method of depicting the critical path in project scheduling. It places constraints on other activities in order to make sure that they do not interfere with the main schedule. It also tells at what stage each activity must be completed to ensure that the overall completion date meets or exceeds target dates.
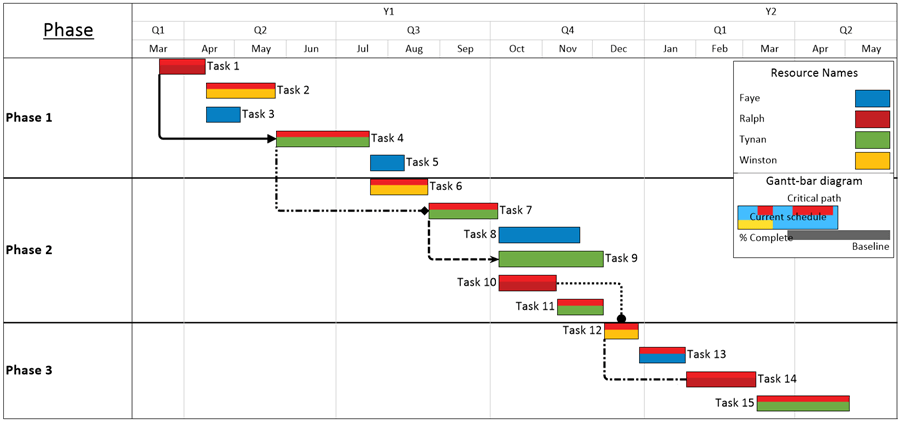
Source: onepager.com
Wrapping Up: Why Scheduling Matters in Project Management
Project scheduling is a very important part of project management, meeting certain criteria to ensure that each task’s work is complete at the right time, and at the right cost.
Through project scheduling, you can see how all separate tasks come together to create the final product or deliverable. The closer you look at each step, the clearer it becomes what each activity is contributing to the whole and why it takes as long as it does.
Why is project scheduling so important? What separates an amateur approach to time management from a professional one?
Simply put, professionals are organized, planned, and dedicated to meeting deadlines. They use Gantt charts, word breakdown templates, critical path schedules and other tools to treat each task with the utmost importance and utilize their time efficiently to minimize silo effects.
A silo effect occurs when there is no cross-collaboration between team members or departments. If individual team members do not communicate with each other or their superiors, it can be extremely difficult for that person to complete their tasks in a timely manner.
On the other hand, silo effects are avoided when staff are able to understand how their work contributes to the overall objectives of the group.
If you’re getting stuck on your project, then it may be time to schedule a time to re-evaluate your plan. Get the answers you need with this guide.
Questions and Answers about Project Scheduling
1. What is the first step involved in project schedule management?
Project schedule management involves preparing a project schedule as well as monitoring and controlling the project schedule. The first step of this process is to break down a project’s scope of work into smaller, manageable pieces. These pieces are known as tasks and they form a critical part of a project schedule.
There are several good reasons for breaking your project down into smaller tasks:
- It makes it easier to visualize how your project will be completed
- It helps you see the bigger picture of how all the different parts fit together
- It allows you to prioritize work by importance and deadlines
2. What is the difference between a project schedule and a project plan?
A project schedule is simply a timeline of the major tasks that you need to complete your project. The project plan, on the other hand, is a document that provides a deeper look into how you intend to complete each task. It lists the resources required, describes how it will be completed, and also includes schedules for all activities.
3. What is float in a project schedule?
Float refers to the amount of time needed to complete the scheduled activities, beyond scheduled work hours. For example, if a project schedule estimates that a task will take 8 hours, but it actually takes 12 hours to complete, the float would be 4 hours.
4. What are the two categories of schedule risk?
- Schedule duration risk. This is when changes in activities cause delays in completing milestones in the schedule for a project. For example, if a task required four days to complete and is delayed, then that task delay will push other tasks forward or delay them as well.
- Schedule effort risk. This is when changes in resource availability cause delays in completing milestones in the schedule for a project.
5. How is uncertainty in project scheduling dealt with?
Rescheduling is a common strategy used to manage uncertainty in project schedules. Rescheduling involves changing the schedule to fit new information such as changes in resources (reserving slots for additional resources). Rescheduling can occur with, for example, reallocating resource time slots – delivering more work – or shifting resources – delivering less work – from one task to another.
6. What are some reasons for updating a project schedule?
- Changes in resources
- Changes in cost
- Change in actual working time.